
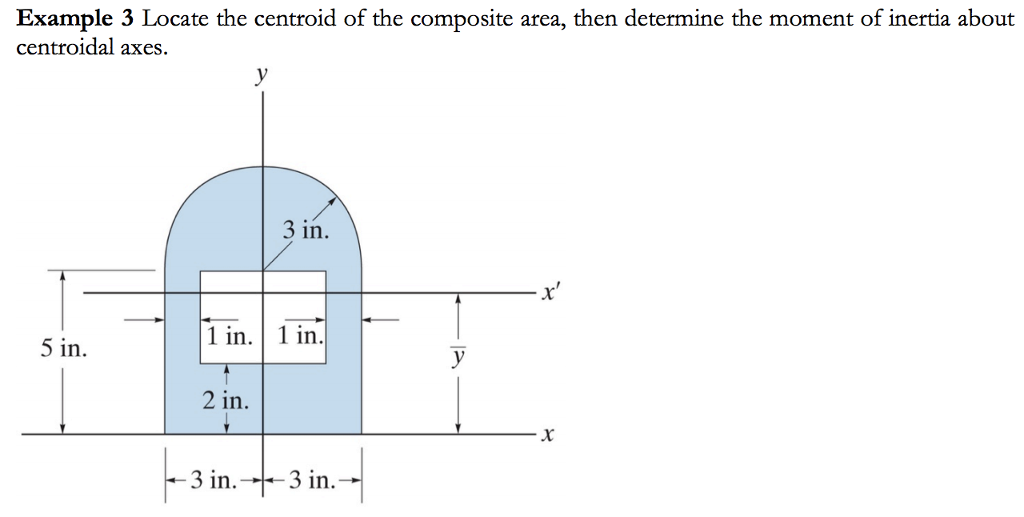
D is said to be the perpendicular distance between the x and x’ axes.I x = moment of inertia in arbitrary axis.If we recognize the moment of inertia of the non-centroidal axis with respect to a centroidal axis parallel to the first, we can find it here. The parallel axis theorem could be used to calculate the area moment of inertia of any shape present in any parallel axis.
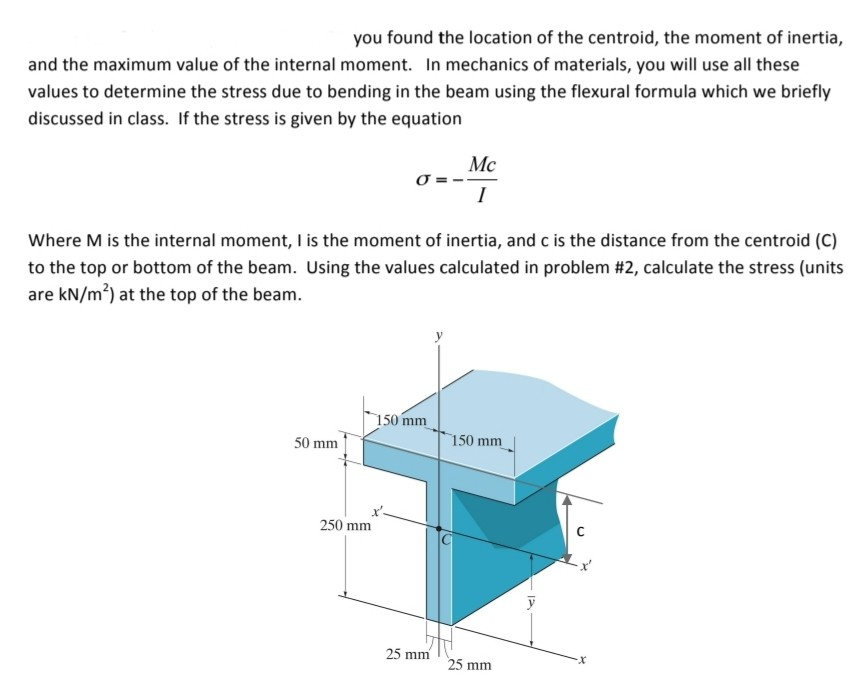
It is seamlessly determined by applying the Parallel Axis Theorem because the rectangle centroid is located at a distance equal to h/2 from the base.
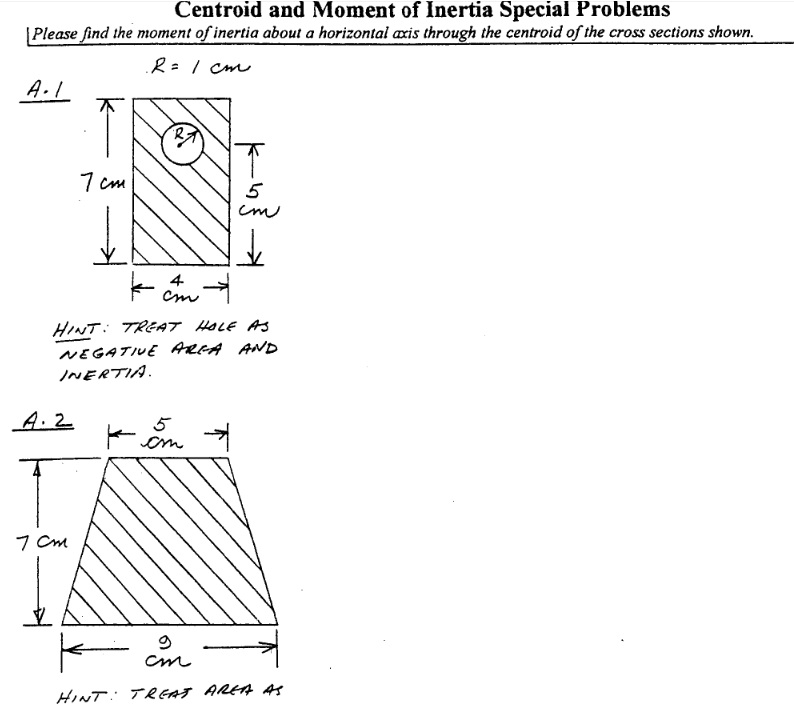
The moment of inertia of a rectangle has been expressed as follows when an axis passes through the base: (2) Moment of Inertia of Rectangle An Axis Passing Through Its Base The rectangle width (a dimension parallel to the axis) has been denoted by b, and the height is denoted by h (dimension perpendicular to the axis).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
